Navigating the complexities of autism and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can be a demanding journey for both individuals and their families. When these two conditions occur together, they form a unique neurodivergent experience often referred to as AuDHD. Understanding the nuances of AuDHD is crucial for offering meaningful support, especially as each person’s needs and traits can vary significantly. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the overlapping characteristics, common challenges, and distinctive features of AuDHD while also exploring emerging treatment options like TMS for ADHD, which are gaining attention for their potential to enhance focus, mood, and overall quality of life in those affected.
Shared Traits of Autism and ADHD
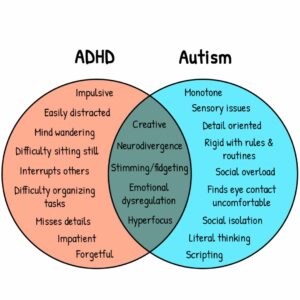
At the core of AuDHD are overlapping traits that complicate diagnosis and understanding. Both autism and ADHD present challenges related to attention, impulsivity, and social interactions. Individuals may find it difficult to focus on tasks, exhibit impulsive behaviors, or navigate social settings effectively. These shared traits necessitate a nuanced understanding to ensure appropriate interventions and support systems are established. For those exploring alternative therapies, searching for tms treatment for autism near me may open doors to emerging non-invasive options designed to support neurological and behavioral improvement.
Challenges in Executive Functioning
Executive functioning encompasses the mental processes that enable individuals to plan, focus attention, remember instructions, and manage multiple tasks simultaneously. For those with AuDHD, difficulties in executive functioning can significantly affect daily life. Many individuals struggle with organizing tasks, managing time efficiently, and regulating their emotions. Consequently, they may feel overwhelmed by everyday responsibilities. Addressing these challenges through targeted strategies and interventions is crucial for promoting independence and self-confidence.
Navigating Social Interaction Hurdles
Social interactions present unique challenges for individuals with AuDHD. They may find it difficult to interpret social cues, engage in reciprocal conversations, or navigate the dynamics of group settings. This struggle can lead to feelings of isolation, frustration, and anxiety. Understanding the unique social needs of individuals with AuDHD is essential for fostering supportive environments, whether in educational contexts, workplaces, or social gatherings.
Create a video discussing the key aspects of AuDHD, featuring interviews with individuals who share their personal experiences. Include insights from mental health professionals and tips for navigating social challenges associated with autism and ADHD.
Understanding Sensory Sensitivities
Sensory sensitivities are often a hallmark of both Autism and ADHD. Individuals with AuDHD may experience heightened sensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, textures, or smells. This sensitivity can lead to overwhelming experiences in everyday environments, making it essential to create spaces that accommodate sensory needs. Acknowledging these sensitivities allows caregivers, educators, and peers to develop supportive environments that minimize discomfort and promote well-being. Additionally, accessing resources such as Anxiety Disorder Treatment Fort Lee NJ can further support individuals in managing their sensory experiences effectively.
Distinctive Features of AuDHD
Living with AuDHD encompasses a range of distinctive features that set it apart from autism and ADHD when considered in isolation. Understanding these features can enhance the support provided to individuals with AuDHD.
- Seeking New Experiences While Feeling Anxious: Individuals may crave novelty and change but simultaneously feel overwhelmed by new situations. This internal conflict can create significant stress and anxiety, making it challenging to engage in new experiences fully.
- Creating Routines Yet Struggling with Consistency: Many individuals with AuDHD find comfort in establishing routines. However, maintaining these routines over time can be challenging, leading to feelings of frustration and self-doubt.
- Thriving in Organized Spaces Amid Chaos: While individuals may excel in organized environments, they may also find themselves surrounded by chaos in other areas of their lives. This paradox can lead to a sense of internal conflict as they navigate their surroundings.
- Balancing Special Interests with Shifting Fascinations: Those with AuDHD often possess enduring special interests, yet they may also experience rapidly changing fascinations. This fluctuation can contribute to feelings of instability as interests evolve.
- Feeling Drained from Social Activities: Social engagements can be exhausting for individuals with AuDHD, leading to burnout. Despite this, they may find it difficult to prioritize self-care and take time for rest and recovery.
- Appreciating Structure but Struggling in Group Settings: Many individuals thrive in structured environments, such as schools or workplaces. However, they may find it challenging to navigate group settings, where social dynamics can become overwhelming.
The Individual Nature of AuDHD
One of the most critical aspects of AuDHD is recognizing that no two individuals share the same experience. Each person brings a unique combination of traits, challenges, and coping mechanisms. This individuality underscores the importance of personalized support and intervention strategies tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual.
Emotional Regulation Challenges
Emotional regulation often presents significant challenges for individuals with AuDHD. They may experience intense emotions that can fluctuate rapidly, leading to difficulties in managing their responses to stress or anxiety. Recognizing and understanding these emotional patterns is essential for developing effective coping strategies. Implementing mindfulness techniques, cognitivebehavioral strategies, and support from mental health professionals can help individuals better navigate their emotional landscapes.
Communication Styles: Differences in Verbal and Non-Verbal Interactions
Communication styles can vary significantly for individuals with AuDHD. Some may excel in verbal communication, while others might express themselves more effectively through non-verbal means, such as art or writing. Understanding these diverse communication styles is essential for fostering connections and promoting effective interactions. Creating environments that encourage open communication and provide various outlets for expression can significantly enhance social engagement and relationships.
The Role of Routine
For many individuals with AuDHD, routines play a vital role in providing a sense of predictability and stability. Routines can help mitigate anxiety and create a sense of normalcy in an often chaotic world. However, the fear of change can also pose a significant hurdle. Developing flexible routines that allow for adaptation while maintaining structure can empower individuals to embrace new experiences without feeling overwhelmed.
Coping Mechanisms for Managing Overwhelm and Burnout
Managing overwhelm and burnout is crucial for individuals with AuDHD. Implementing effective coping mechanisms, such as time management techniques, mindfulness practices, and self-care routines, can help alleviate stress levels. Encouraging individuals to identify their triggers and develop personalized strategies for managing anxiety can lead to more balanced and fulfilling lives.
Self-Advocacy: Navigating Needs and Rights
Self-advocacy is an essential skill for individuals with AuDHD. Understanding their rights and needs empowers them to seek appropriate support and accommodations in various settings, including educational and workplace environments. Empowering individuals to express their needs fosters confidence and autonomy, enabling them to navigate challenges more effectively.
Support Systems: Finding the Right Resources and Community
Creating a robust support system is critical for individuals with AuDHD. Support can come in many forms, including therapy, peer groups, family, and community resources. Accessing resources, such as an adult ADHD test, Autism Treatment New Jersey, and connecting with local organizations can provide valuable assistance for individuals and their families. Building a network of support can foster a sense of belonging and understanding, which is crucial for navigating the complexities of AuDHD.
Conclusion
Understanding AuDHD requires a multifaceted approach that recognizes the unique challenges and strengths of individuals living with both autism and ADHD. Tools such as the autism spectrum quotient can help capture the range of autistic traits—across domains like social skills, communication, imagination, attention to detail, and flexibility providing insight into an individual’s experience and guiding more tailored support strategies WikipediaBioMed Central. By acknowledging shared traits, challenges, and distinctive features, we can provide more effective support and foster inclusive environments. The journey of individuals with AuDHD is complex and deeply personal, emphasizing the need for tailored interventions and compassionate understanding of their experiences. Emerging therapies, including transcranial magnetic stimulation adhd, show promise meta‑analyses indicate that rTMS interventions can significantly improve core ADHD symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, with positive effects lasting up to a month or more and only minor adverse effects reported PMCPubMed. Visiting a TMS wellness center may offer additional support through such non‑invasive therapies designed to enhance focus, emotional regulation, and cognitive clarity. Additionally, exploring methods such as How TMS Therapy Transforms the Treatment of Manic Episodes in Bipolar Disorder can enhance our understanding of effective support strategies. As we strive to create a more inclusive society, let us remember that each individual’s journey is unique, deserving of respect and empathy.